Correctly label the following anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint – Correctly labeling the anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint is essential for accurate diagnosis, surgical planning, and effective communication among healthcare professionals. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the tibiofemoral joint’s anatomy, clinical significance, labeling methods, and educational resources.
Introduction: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Tibiofemoral Joint
The tibiofemoral joint, also known as the knee joint, is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in human movement. Correctly labeling its anatomical features is essential for accurate communication among healthcare professionals, surgical procedures, and patient outcomes.
Anatomical Features of the Tibiofemoral Joint
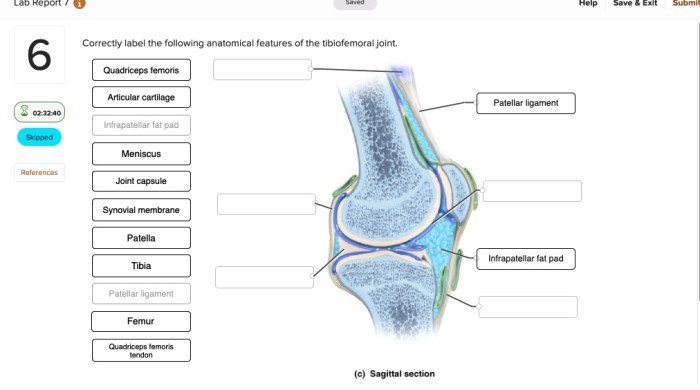
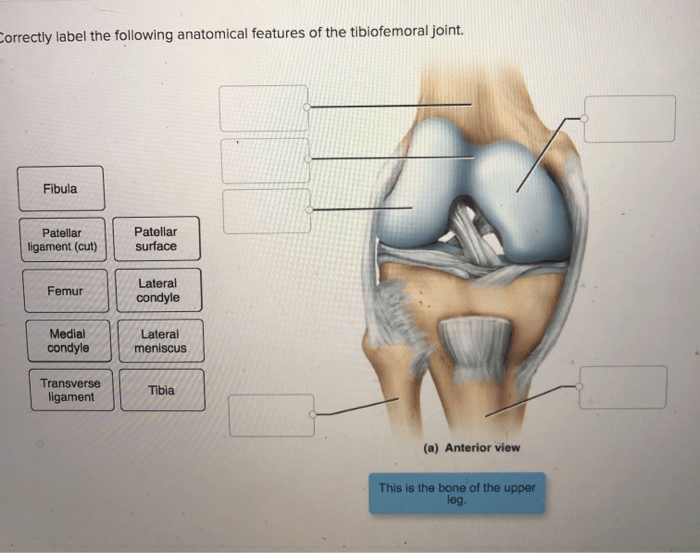
Medial and Lateral Condyles of the Femur
The medial and lateral condyles of the femur are the rounded projections at the distal end of the femur that articulate with the tibia. They provide stability and allow for flexion and extension of the knee.
Medial and Lateral Menisci, Correctly label the following anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint
The medial and lateral menisci are C-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that sit between the femur and tibia. They act as shock absorbers, provide stability, and deepen the joint surfaces for better load distribution.
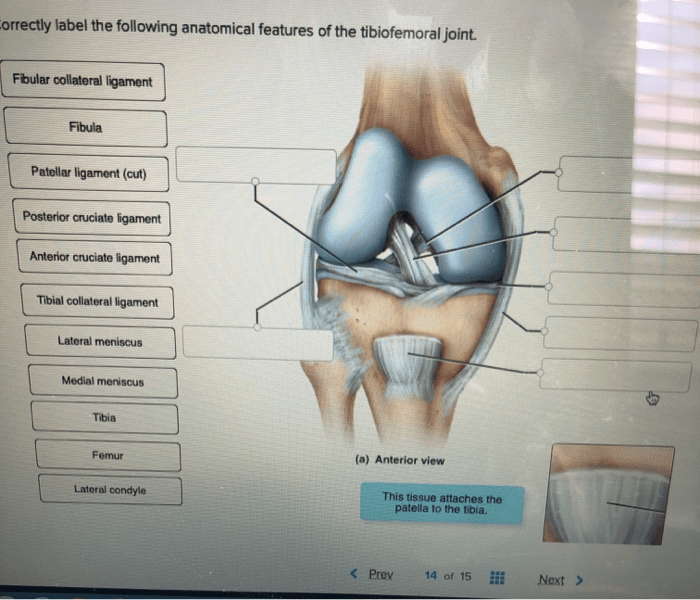
Anterior and Posterior Cruciate Ligaments
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are strong bands of tissue that cross each other within the knee joint. They prevent excessive anterior and posterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur, providing stability during various movements.
Tibial and Fibular Collateral Ligaments
The tibial collateral ligament (MCL) and fibular collateral ligament (LCL) are located on the medial and lateral sides of the knee joint, respectively. They prevent excessive medial and lateral displacement of the tibia, providing stability during side-to-side movements.
Clinical Significance of Correct Labeling
Mislabeling anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint can have significant implications:
- Surgical Procedures:Incorrect labeling can lead to inaccurate surgical plans and potential complications during surgery.
- Patient Outcomes:Mislabeled anatomical features can result in incorrect diagnoses, inappropriate treatment, and delayed recovery.
- Communication:Accurate labeling ensures clear and precise communication among healthcare professionals, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and errors.
Methods for Labeling Anatomical Features
Various methods are used to label anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint:
- Gross Anatomy Dissection:Direct examination of cadavers allows for detailed visualization and labeling of anatomical structures.
- Imaging Techniques:MRI and CT scans provide non-invasive methods for visualizing and labeling anatomical features in vivo.
- Surgical Exploration:During surgical procedures, surgeons can directly observe and label anatomical structures.
Educational Resources for Correct Labeling
To facilitate accurate labeling, various educational resources are available:
- Anatomy Textbooks:Provide comprehensive descriptions and illustrations of anatomical features.
- Online Anatomy Atlases:Offer interactive 3D models and images for exploring and labeling anatomical structures.
- Cadaveric Dissection Workshops:Provide hands-on experience in dissecting and labeling anatomical features.
Questions Often Asked
Why is it important to correctly label the anatomical features of the tibiofemoral joint?
Correct labeling facilitates precise communication among healthcare professionals, ensures accurate surgical planning, and enhances patient outcomes.
What are the common methods used to label anatomical features?
Gross anatomy dissection, imaging techniques (MRI, CT scans), and surgical exploration are commonly used methods for labeling anatomical features.
Where can I find resources for learning and practicing the correct labeling of anatomical features?
Anatomy textbooks, online anatomy atlases, and cadaveric dissection workshops provide valuable resources for learning and practicing correct labeling.