Delving into which of the following pure compounds will exhibit hydrogen bonding, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence. Hydrogen bonding is a crucial intermolecular force that plays a significant role in various scientific disciplines, and this exploration will shed light on its fundamental principles and applications.
The subsequent paragraphs will provide a comprehensive analysis of hydrogen bonding, including its definition, characteristics, and the specific compounds that exhibit this unique interaction. We will also delve into the impact of hydrogen bonding on the physical properties of substances and its applications in chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Hydrogen Bonding: Definition and Characteristics
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules that contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. The hydrogen atom in the hydrogen bond is partially positive, and the electronegative atom is partially negative.
This creates an electrostatic attraction between the two molecules.
Pure Compounds Exhibiting Hydrogen Bonding
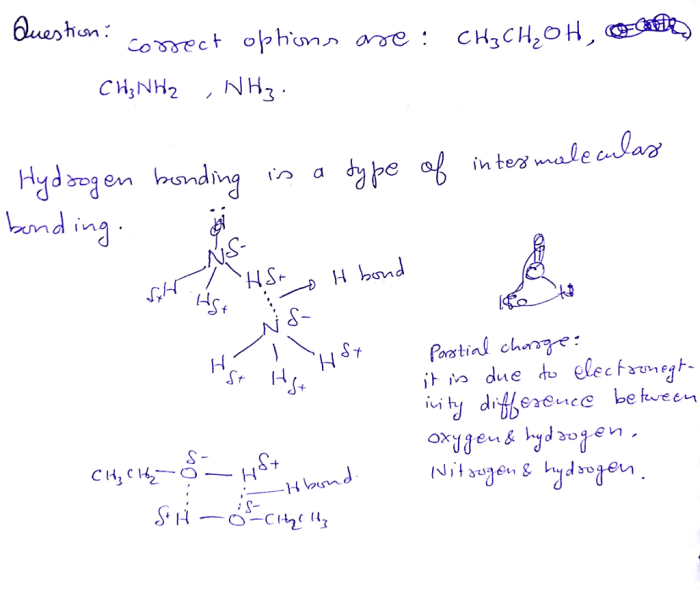
Pure compounds that exhibit hydrogen bonding include:
- Water (H 2O)
- Ammonia (NH 3)
- Hydrogen fluoride (HF)
- Ethanol (CH 3CH 2OH)
- Acetic acid (CH 3COOH)
Examples of Hydrogen Bonding in Different States of Matter
Hydrogen bonding can occur in all three states of matter:
- In liquids, hydrogen bonding can lead to the formation of dimers and other small clusters of molecules. These clusters can affect the physical properties of the liquid, such as its viscosity and boiling point.
- In solids, hydrogen bonding can lead to the formation of crystals. The strength of the hydrogen bonds determines the melting point of the solid.
- In gases, hydrogen bonding can occur between molecules that are close together. This can affect the physical properties of the gas, such as its viscosity and thermal conductivity.
Applications of Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding has a wide range of applications in different fields, including:
- Chemistry:Hydrogen bonding is used in the design of new materials, such as polymers and pharmaceuticals.
- Biology:Hydrogen bonding is essential for the structure and function of biological molecules, such as DNA and proteins.
- Materials science:Hydrogen bonding is used in the development of new materials, such as self-assembling materials and biomaterials.
Comparison of Hydrogen Bonding with Other Intermolecular Forces: Which Of The Following Pure Compounds Will Exhibit Hydrogen Bonding

Hydrogen bonding is stronger than other intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. This is because hydrogen bonding involves a partial covalent bond, while van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions are non-covalent.
Influence of Hydrogen Bonding on Molecular Structure and Properties
Hydrogen bonding can affect the molecular structure and properties of compounds. For example, hydrogen bonding can lead to the formation of dimers and other small clusters of molecules. This can affect the physical properties of the compound, such as its viscosity and boiling point.
Role of Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Systems
Hydrogen bonding is essential for the structure and function of biological molecules. For example, hydrogen bonding is responsible for the double helix structure of DNA and the tertiary structure of proteins.
Methods for Detecting Hydrogen Bonding

There are a number of experimental techniques that can be used to detect hydrogen bonding in compounds. These techniques include:
- Infrared spectroscopy
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
- X-ray crystallography
Common Queries
What is the definition of hydrogen bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is an attractive intermolecular force that occurs between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another electronegative atom.
Which pure compounds exhibit hydrogen bonding?
Pure compounds that exhibit hydrogen bonding include water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and alcohols (ROH).
How does hydrogen bonding affect the physical properties of substances?
Hydrogen bonding can affect the physical properties of substances by increasing their boiling points, melting points, and viscosity.