Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of biomes with our comprehensive Exploring Biomes Worksheet Answer Key. This meticulously crafted resource unravels the intricacies of Earth’s diverse ecosystems, providing an unparalleled understanding of the interactions that shape our planet’s natural tapestry.
Through an engaging narrative and a wealth of supporting materials, this worksheet answer key illuminates the defining characteristics of biomes, their global distribution, and the complex interplay between biotic and abiotic factors within these vital ecosystems.
Biome Definition and Characteristics
A biome is a large-scale ecological community characterized by distinct climate, vegetation, and animal life. It represents a major terrestrial or aquatic ecosystem, encompassing various ecosystems and communities within it.
Biomes are classified based on several key characteristics, including climate, soil type, vegetation structure, and animal adaptations. These characteristics are influenced by latitude, altitude, precipitation, temperature, and other environmental factors.
Classification and Differentiation
Biomes are differentiated from each other by their unique combinations of these characteristics. For example, tropical rainforests are characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation, while deserts are characterized by low precipitation, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
The classification of biomes is a complex and ongoing process, as scientists continue to refine their understanding of ecological communities and their interactions with the environment.
Major Biomes of the World
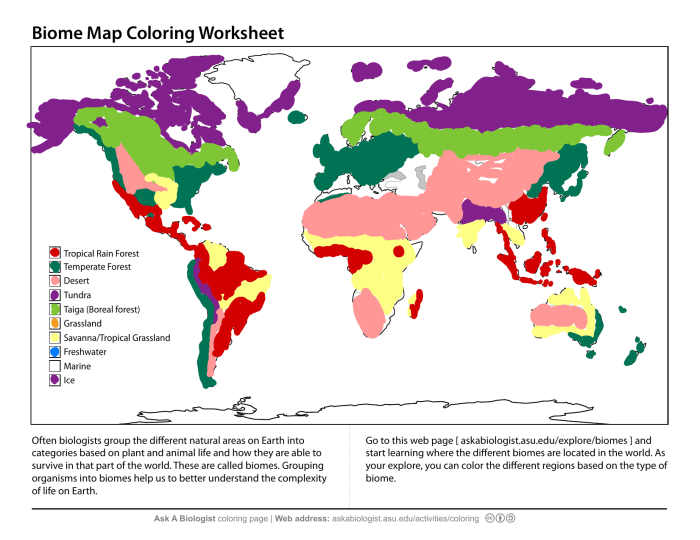
The Earth’s surface is covered by a wide variety of biomes, each with its own unique set of climatic conditions, vegetation, and animal life. The major biomes of the world include:
- Tropical Rainforest:Found near the equator, tropical rainforests are characterized by warm, humid climates with abundant rainfall. They are home to a wide variety of plant and animal life, including many endangered species.
- Temperate Rainforest:Found in coastal areas of the Pacific Northwest and New Zealand, temperate rainforests are characterized by mild, wet climates with moderate rainfall. They are home to a variety of coniferous and broadleaf trees, as well as a variety of animals, including bears, wolves, and elk.
- Temperate Deciduous Forest:Found in eastern North America, Europe, and Asia, temperate deciduous forests are characterized by warm, humid summers and cold, dry winters. They are home to a variety of deciduous trees, as well as a variety of animals, including deer, squirrels, and rabbits.
- Boreal Forest:Found in northern North America, Europe, and Asia, boreal forests are characterized by cold, dry climates with long, snowy winters. They are home to a variety of coniferous trees, as well as a variety of animals, including moose, caribou, and wolves.
- Grassland:Found in central North America, South America, and Asia, grasslands are characterized by warm, dry climates with moderate rainfall. They are home to a variety of grasses, as well as a variety of animals, including bison, antelope, and prairie dogs.
- Desert:Found in the southwestern United States, Mexico, and North Africa, deserts are characterized by hot, dry climates with little rainfall. They are home to a variety of cacti, succulents, and other plants that are adapted to dry conditions, as well as a variety of animals, including snakes, lizards, and scorpions.
- Tundra:Found in the Arctic and Antarctic regions, tundra is characterized by cold, dry climates with long, cold winters. They are home to a variety of mosses, lichens, and other plants that are adapted to cold conditions, as well as a variety of animals, including reindeer, caribou, and polar bears.
- Mediterranean Climate:Found in the Mediterranean region, the Mediterranean climate is characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. They are home to a variety of evergreen trees and shrubs, as well as a variety of animals, including olive trees, grapes, and sheep.
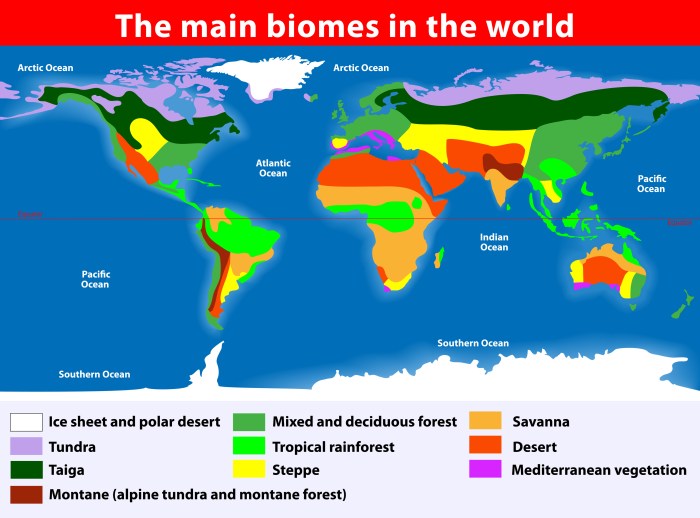
The distribution of biomes around the world is influenced by a variety of factors, including latitude, altitude, and distance from the ocean. The map below shows the distribution of the major biomes of the world.[Insert map or diagram of the distribution of biomes globally]
Interactions within Biomes
Within biomes, intricate interactions occur between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors, shaping the structure and function of ecosystems. These interactions include energy flow through food webs, nutrient cycling, and competition for resources.
Biotic Interactions
Biotic interactions encompass the relationships between organisms within a biome. These relationships can be positive, negative, or neutral. Examples include:
- Competition:Organisms compete for limited resources such as food, water, and sunlight, leading to niche partitioning and resource specialization.
- Predation:Predators consume prey, controlling prey populations and influencing community structure.
- Symbiosis:Close relationships between different species, such as mutualism (both species benefit), commensalism (one species benefits while the other is unaffected), and parasitism (one species benefits at the expense of the other).
Abiotic Interactions
Abiotic factors, such as temperature, precipitation, soil type, and sunlight, influence the distribution and abundance of organisms within biomes. Examples include:
- Temperature:Different species have specific temperature tolerances, limiting their distribution to certain areas.
- Precipitation:Rainfall and snowfall affect plant growth, water availability, and erosion rates.
li> Soil type:Soil pH, texture, and nutrient content determine which plants can thrive in a particular area.
Food Webs and Nutrient Cycles
Food webs depict the flow of energy through an ecosystem, with producers (plants) converting sunlight into energy and consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers) utilizing that energy. Nutrient cycles, such as the nitrogen and carbon cycles, describe the movement of essential nutrients through ecosystems, ensuring their availability for organisms.
Human Impact on Biomes: Exploring Biomes Worksheet Answer Key
Human activities have a significant influence on the health and biodiversity of biomes worldwide. Both positive and negative impacts result from human interactions with the environment, ranging from habitat loss and pollution to climate change.
Habitat Loss, Exploring biomes worksheet answer key
Habitat loss occurs when natural areas are converted for human uses such as agriculture, urbanization, or mining. This fragmentation and destruction of habitats can lead to a decline in biodiversity as species lose their homes and resources.
For example, the conversion of tropical rainforests to farmland has resulted in the loss of habitat for numerous plant and animal species, including endangered animals like the Sumatran tiger and orangutan.
Pollution
Pollution, including air, water, and soil contamination, can have detrimental effects on biomes. Industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and vehicle emissions can release harmful substances into the environment, which can accumulate in organisms and disrupt ecosystems.
Pollution can cause respiratory problems, damage to aquatic life, and contamination of food chains. For instance, air pollution from industrial emissions has been linked to respiratory issues in urban areas, while agricultural runoff containing fertilizers and pesticides has led to algal blooms and fish kills in waterways.
Climate Change
Climate change, primarily caused by the release of greenhouse gases, is altering the temperature, precipitation patterns, and sea levels globally. These changes can have profound impacts on biomes, affecting species distributions, ecosystem functioning, and biodiversity.
For example, rising temperatures in the Arctic are causing sea ice to melt, threatening the habitat of polar bears and other Arctic species. Additionally, changes in precipitation patterns can lead to droughts or floods, which can disrupt plant growth and water availability for wildlife.
Conservation and Management of Biomes

Conserving and managing biomes is crucial for maintaining the health and functioning of the Earth’s ecosystems. Biomes provide essential services such as climate regulation, water purification, and biodiversity conservation. However, human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, and pollution pose significant threats to biomes worldwide.Effective
conservation and management of biomes require a multifaceted approach involving protected areas, sustainable land use practices, and restoration efforts. Protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, safeguard critical habitats and prevent their conversion to other uses. Sustainable land use practices, such as agroforestry and conservation agriculture, aim to minimize the negative impacts of human activities on biomes while maintaining productivity.
Restoration efforts focus on rehabilitating degraded biomes and restoring their ecological functions.
Successful Conservation Initiatives
Numerous successful conservation initiatives have been implemented in different biomes worldwide. In the Amazon rainforest, the establishment of protected areas and the implementation of sustainable logging practices have helped reduce deforestation rates. In the Great Barrier Reef, marine protected areas and efforts to reduce pollution have contributed to the recovery of coral populations.
In the African savanna, community-based conservation initiatives have empowered local communities to protect wildlife and their habitats. These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of collaborative efforts involving governments, conservation organizations, and local communities in conserving and managing biomes.
Popular Questions
What is the primary purpose of a biome?
Biomes serve as fundamental units of Earth’s ecosystems, characterized by unique combinations of climate, vegetation, and animal life that shape the structure and function of each ecosystem.
How are biomes classified?
Biomes are classified based on their dominant vegetation type, which is primarily influenced by climate factors such as temperature, precipitation, and sunlight availability.
What are the major threats facing biomes today?
Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species pose significant threats to the health and biodiversity of biomes worldwide.